AngularJS with Backend Example
Hello readers, in this basic example, developers will learn what AngularJS is and how to make AJAX calls to a Servlet using the AngularJS controller and update the view back with the JSON response from the Servlet.
1. Introduction
1.1 What is AngularJS?
AngularJS is a JavaScript MVC or Model-View-Controller framework developed by Google that lets developers build well structured, easily testable, and maintainable front-end applications. Before we start with creating an actual application using AngularJS, let us see what the actual parts of an AngularJS application are.
1.1.1 Templates
In AngularJS, a template is an HTML with additional markups. AngularJS library compiles the templates and renders the resultant HTML page.
1.1.2 Directives
Directives are the markers (i.e. attributes) on a DOM element that tell AngularJS to attach a specific behavior to that DOM element or even transform the DOM element and its children. Most of the directives in AngularJS library starts with the ng. The directives consist of the following three parts:
ng-app: Theng-appdirective is a starting point. If the AngularJS framework finds theng-appdirective anywhere in theHTMLdocument, it bootstraps (i.e. initializes) itself and compiles theHTMLtemplateng-model: Theng-modeldirective binds anHTMLelement to a property on the$scopeobject. It also binds the values of AngularJS application data to theHTMLinput controls.ng-bind: Theng-binddirective binds the AngularJS application data to theHTMLtagsng-controller: Theng-controllerdirective is used to specify a controller in theHTMLelement. This controller will add behavior or maintain the data in thatHTMLelement and its child elements
1.1.3 Expressions
An expression is like a JavaScript code which is usually wrapped inside the double curly braces such as {{ expression }}. AngularJS library evaluates the expression and produces a result.
The following table lists all the important concepts in AngularJS library.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Template | An HTML with additional markups. |
| Directives | Extends the HTML with the custom attributes (or markers) and elements. |
| Model | It is the data shown to the user in the view with which the user interacts. |
| Scope | A Scope is a context where the model is stored so that controllers, directives, and expressions can access it. |
| Expressions | An expression executes the JavaScript code inside the double curly braces such as {{ expression }}. |
| Compiler | The Compiler parses the template and instantiates the directives and expressions. |
| Filter | A Filter formats the value of an expression for display to the user. |
| Data Binding | This syncs the data between the model and the view. |
| Controller | A controller in AngularJS maintains the application data, business logic, and behavior using the $scope object. Developers can attach properties and methods to the $scope object inside a controller function, which in turn will add or update the data and attach behaviours to the HTML elements. |
| Module | The module is the container for different parts of an application including the controllers, services, filters, and directives which configures the Injector. |
| Service | A Service is reusable business logic which is independent of the views. |
1.2 Why should we use AngularJS?
Using the Model-View-Controller architecture, the framework separates a web application into a simple and yet manageable structure, which comprises of “views”, “models” and “controllers”. The AngularJS library provides the in-build directives (or attributes) to extend the HTML inside a web page. When developers attach these directives to the HTML elements and attributes, it creates a dynamic web-page with very little coding.
These new APIs make a developer life easier, really! But it would be difficult for a beginner to understand this without an example. Therefore, let’s see how to integrate AngularJS in Java web applications.
2. AngularJS with Backend Example
Here is a step-by-step guide for implementing the AngularJS framework in Java.
2.1 Tools Used
We are using Eclipse Kepler SR2, JDK 8 and Maven.
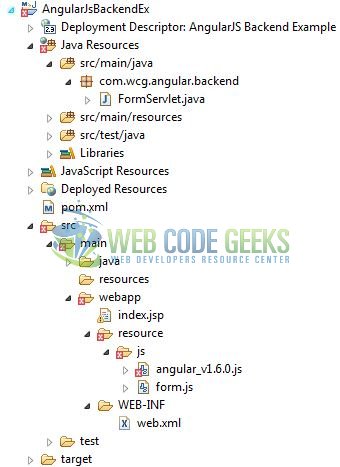
2.2 Project Structure
Firstly, let’s review the final project structure, in case you are confused about where you should create the corresponding files or folder later!
2.3 Project Creation
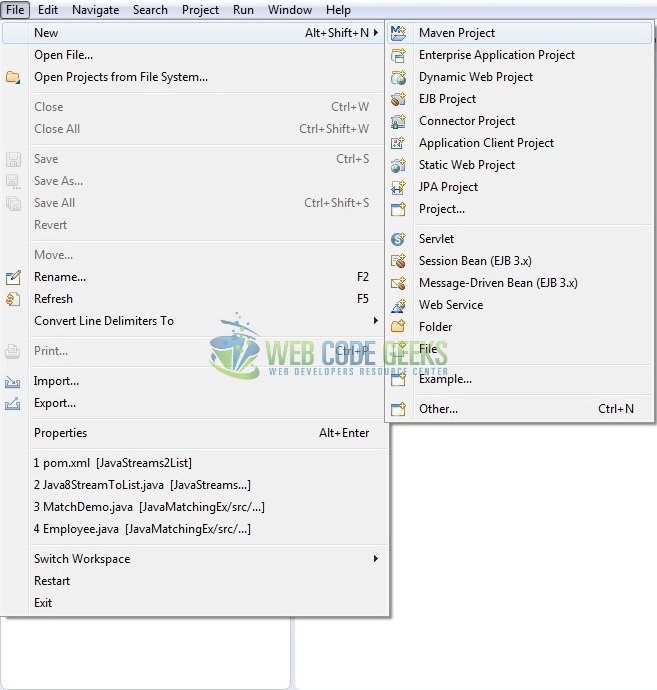
This section will demonstrate on how to create a Java-based Maven project with Eclipse. In Eclipse Ide, go to File -> New -> Maven Project.
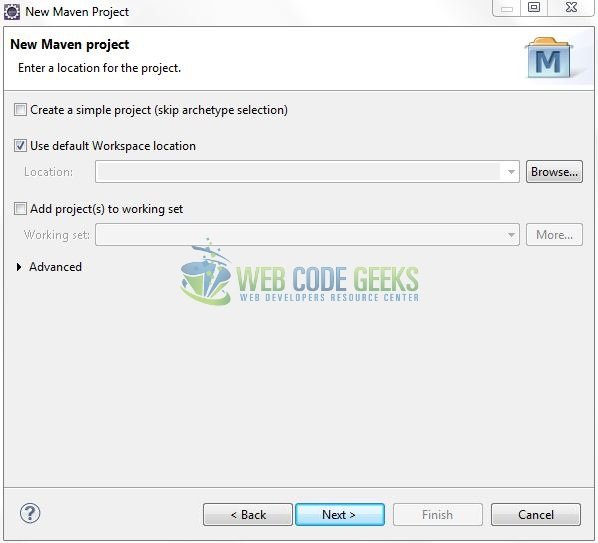
In the New Maven Project window, it will ask you to select project location. By default, ‘Use default workspace location’ will be selected. Just click on next button to proceed.
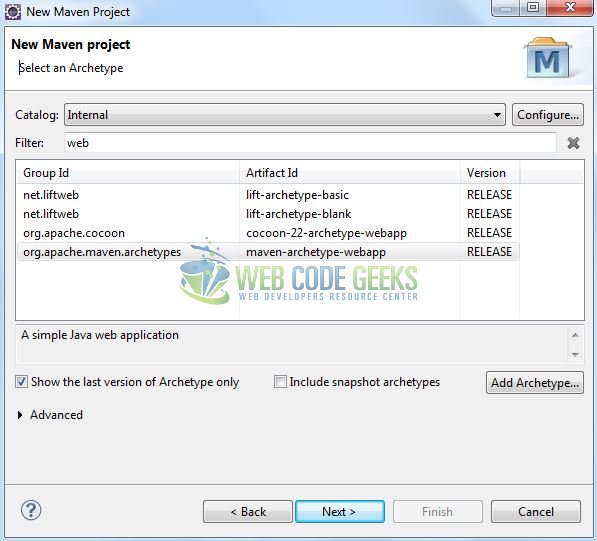
Select the ‘Maven Web App’ Archetype from the list of options and click next.
It will ask you to ‘Enter the group and the artifact id for the project’. We will input the details as shown in the below image. The version number will be by default: 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.

Click on Finish and the creation of a maven project is completed. If you observe, it has downloaded the maven dependencies and a pom.xml file will be created. It will have the following code:
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>AngularJsBackendEx</groupId> <artifactId>AngularJsBackendEx</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> </project>
Let’s start building the application!
3. Application Building
Let’s create a basic welcome application to understand the basic building blocks of AngularJS library.
3.1 Maven Dependencies
Here, we specify the dependencies for the Servlet and JSON API. The rest dependencies will be automatically resolved by the Maven framework and the updated file will have the following code:
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>AngularJsBackendEx</groupId>
<artifactId>AngularJsBackendEx</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>AngularJsBackendEx Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<dependencies>
<!-- Servlet API Dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.json/json -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.json</groupId>
<artifactId>json</artifactId>
<version>20160810</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName>
</build>
</project>
3.2 Java Class Creation
Let’s create the required Java files. Right-click on src/main/java folder, New -> Package.
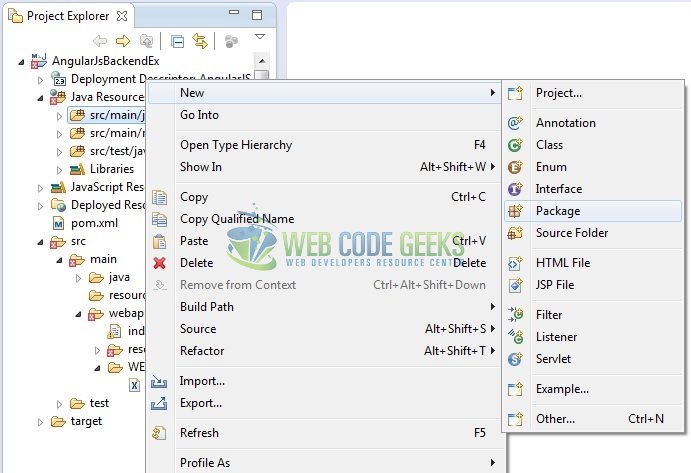
A new pop window will open where we will enter the package name as: com.wcg.angular.backend.
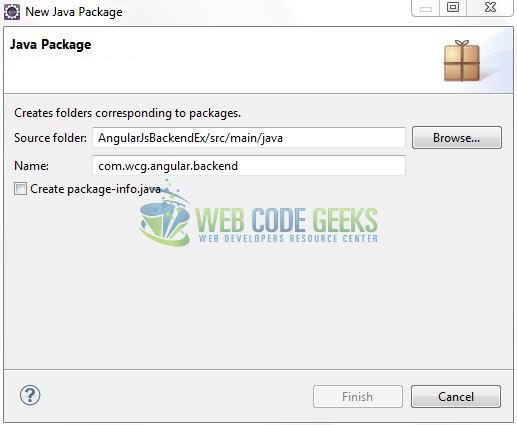
Once the package is created in the application, we will need to create the servlet controller class. Right-click on the newly created package: New -> Class.
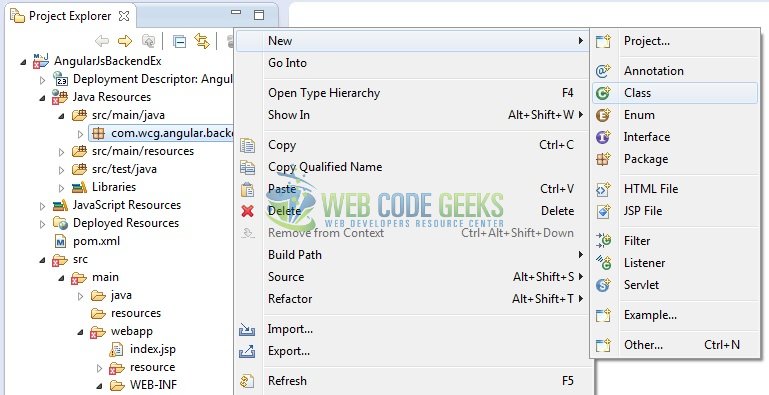
A new pop window will open and enter the file name as: FormServlet. The controller class will be created inside the package: com.wcg.angular.backend.
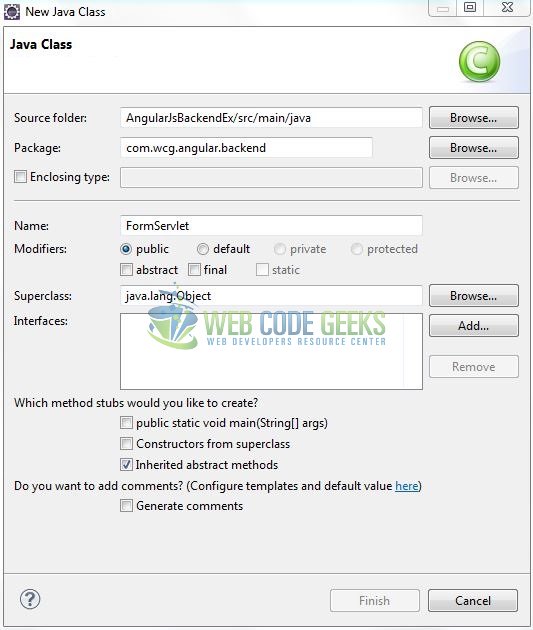
3.2.1 Implementation of Servlet Controller
This is a normal Java servlet except the part that it reads the JSON payload. As the data in angular is not a part of the parameter, hence developers cannot use the getParameter() method in the servlet. Instead, they can get the reader and read all the content before parsing it into the JSON object. Let’s see the simple code snippet that follows this implementation.
FormServlet.java
package com.wcg.angular.backend;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.json.JSONObject;
@WebServlet("/formServlet")
public class FormServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**** This Method Is Called By The Servlet Container To Process A 'POST' Request. ****/
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException {
handleRequest(req, resp);
}
public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException {
String str = null;
StringBuffer sb = null;
JSONObject jObj = null;
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
br = req.getReader();
sb = new StringBuffer();
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(str);
}
jObj = new JSONObject(sb.toString());
String user_name = jObj.getString("username");
/**** Preparing The Output Response ****/
resp.setContentType("text/html");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
resp.getWriter().write("Welcome " + user_name + " !!");
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.3 Creating JSP View
This file is responsible for the AJAX call made to the servlet and for updating the response back in the JSP. Let’s see the simple code snippet to create a simple view using the angular framework.
index.jsp
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>AngularJS Application</title>
<!-- Javascript Files -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="resource/js/angular_v1.6.0.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="resource/js/form.js"></script>
<!-- CSS Styling -->
<style type="text/css">
.cssStyling {
color: green;
font-size: larger;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>AngularJS Backend Application</h1>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<form ng-controller="UserController" ng-submit="sendData()">
<p>
<label>Enter your name: </label>
<input id="user_name" type="text" ng-model="name" placeholder="User Name" onblur="this.placeholder = 'User Name'" onfocus="this.placeholder = ''" />
</p>
<p>
<button id="formBtn" type="submit">Submit</button>
</p>
<!-- Display's Output On The Screen -->
<p>
<span id="welcomeText" class="cssStyling">{{msgFromServlet}}</span>
</p>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
3.3.1 Creating AngularJS Controller
The Javascript file i.e. form.js includes the function (i.e. UserController) as the “controller” in the Model-View-Controller. It submits the form data to the server and reads back the response message to the $scope.msgFromServlet.
form.js
/*
* Description - AngularJS Script for Form Submission
* Created By - Yatin Batra
* */
var helloAjaxApp = angular.module("myApp", []);
helloAjaxApp.controller("UserController", [ '$scope', '$http', function($scope, $http) {
$http.defaults.headers.post["Content-Type"] = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8";
$scope.sendData = function() {
$http({
url : 'formServlet',
method : "POST",
data : {
'username' : $scope.name
}
}).then(function(response) {
/**** Success Case ****/
console.log("Success -> " + response.data);
$scope.msgFromServlet = response.data;
}, function(response) {
/**** Failure Case ****/
console.log("Failure -> " + response.data);
$scope.msgFromServlet = response.data;
});
};
} ]);
4. Run the Application
As we are ready for all the changes, let us compile the project and deploy the application on the Tomcat7 server. To deploy the application on Tomat7, right-click on the project and navigate to Run as -> Run on Server.
Tomcat will deploy the application in its web-apps folder and shall start its execution to deploy the project so that we can go ahead and test it in the browser.
5. Project Demo
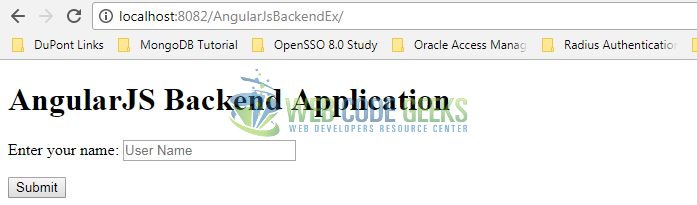
Open your favorite browser and hit the following URL. The output page (i.e. the welcome form) will be displayed.
http://localhost:8082/AngularJsBackendEx/
Server name (localhost) and port (8082) may vary as per your Tomcat configuration. Developers can debug the example and see what happens after every step. Enjoy!
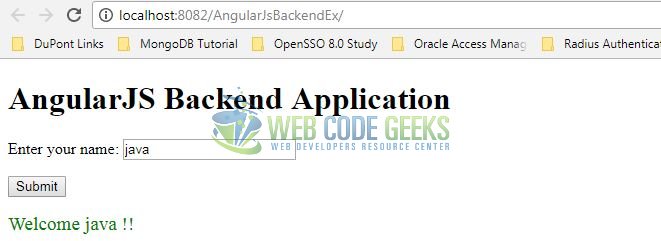
The user enters the name of a person and clicks the Submit button. The data will pass as a HTTP request using the AngularJS and the servlet will return the response as below.
That’s all for this post. Happy Learning!!
6. Conclusion
In this section, developers learned how to create a simple AngularJS enabled Java web application. Developers can download the sample application as an Eclipse project in the Downloads section. I hope this article served you with whatever developers were looking for.
7. Download the Eclipse Project
This was an example of AngularJS with Backend implementation.
You can download the full source code of this example here: AngularJsBackendEx




after creation of a Maven project no src/main/java folder is created (there is only src/main/resources)
I had the same issue, you can create java folder manually under src/main/ folder, or as Yatin specified in creating package snapshot write full path for source folder
Thanks for sharing this valuable information