CSS Pseudo Class Example
In this example we are talking about CSS pseudo-classes concept.
A CSS pseudo-class is a keyword added to selectors that specifies a special state of the element to be selected. For example :hover will apply a style when the user hovers over the element specified by the selector.
A pseudo-class is used to define a special state of an element.
Outside of IE, they have great browser support. In IE land, even IE8, support is pretty barren. However, the IE9 has full support of them.
Below we will have a look at the general structure and then exmaples.
1. Basic Document Setup
Go ahead and create a new html document and add the basic sytnax in it like so:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>CSS Pseudo Class Example</title> </head> <body> <!-- STYLE SECTION --> <style type="text/css"> </style> <!-- HTML SECTION --> </body> </html>
In the HTML section, we will be adding elements and in the style section refer to these elements and use pseudo-classes.
2. Syntax and What’s New in CSS3?
Before applying any of the pseudo classes, here you have the basic syntax to be applied.
selector:pseudo-class {
property: value;
}
In CSS3 apart from pseudo-classes that already existed like :hover, :active, :checked, :default, there are a ton of new pseudo classes. Below you can find most of the new pseudo classes and a short explanation for each of them:
:nth-child(N)– matches elements on the basis of their positions within a parent element’s list of child elements:nth-last-child(N)– matches elements on the basis of their positions within a parent element’s list of child elements:nth-of-type(N)– matches elements on the basis of their positions within a parent element’s list of child elements:nth-last-of-type(N) -matches elements on the basis of their positions within a parent element’s list of child elements
Understanding :nth-child pseudo-class expressions:
:last-child– matches an element that’s the last child element of its parent element:first-of-type– matches the first child element of the specified element type:last-of-type– matches the last child element of the specified element type:only-child– matches an element if it’s the only child element of its parent:only-of-type– matches an element that’s the only child element of its type:root– matches the element that’s the root element of the document:empty– matches elements that have no children:target– matches an element that’s the target of a fragment identifier in the document’s URI:enabled– matches user interface elements that are enabled:disabled– matches user interface elements that are disabled:checked– matches elements like checkboxes or radio buttons that are checked
3. Cases and Examples
3.1 Link-related pseudo class selectors
:link – use this class to add special style to an unvisited link. For example:
<!-- HTML SECTION --> <a class="link" href="#">Link Selector</a>
<style type="text/css">
.link:link{
color: green;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>

:visited – selects links that have already been visited by the current browser. Using the example above:
<style type="text/css">
.link:visited {
color: red;
}
</style>

:hover – when the mouse cursor rolls over a link, that link is in it’s hover state and this will select it.
:active – selects the link while it is being activated (being clicked on or otherwise activated).
<style type="text/css">
.link:hover{
color: #478fc1;
}
.link:active{
color: black;
}
</style>

3.2 Input & link related pseudo class selectors
:focus – selects links that are the current focus of the keyboard. This is not limited to links, but can be used (and really should be used) on inputs and textareas as well. Here is the HTML with an added form to show the example.
<form> <!-- added a form here --> <label>Name</label> <input type="text" placeholder="Name"> <label>E-Mail</label> <input type="text" placeholder="E-Mail"> <label>Address</label> <input type="text" placeholder="Address"> </form>
<style type="text/css">
input:focus{
background-color: #ffffe5;
}
</style>

:target – the target pseudo class is used in conjunction with IDs, and match when the hash tag in the current URL matches that ID. So if you are at URL www.yoursite.com/#home then the selector #home:target will match.
That can be extremely powerful. For example, you can create a tabbed area where the tabs link to hash tags and then the panels “activate” by matching :target selectors and (for example) using z-index to move to the top.
:enabled – selects inputs that are in the default state of enabled and ready to be used.
:disabled – selects inputs that have the disabled attribute. A lot of browsers will make the input a faded out gray, you can control that with this selector.
<form> <!-- added a form here --> <label>Name</label> <input type="text" placeholder="Name"> <label>E-Mail</label> <input type="text" placeholder="E-Mail"> <label>Address</label> <input disabled type="text" placeholder="Address"> <!-- added disabled attribute --> </form>
<style type="text/css">
input:disabled{
background-color: #ccc;
}
</style>

3.3 Position/Number-based pseudo class selectors
:first-child – Selects the first element within a parent.
:last-child – Selects the last element within a parent.
<div> <div><h3>This is a heading.</h3></div> <div><p>This is just a text.</p></div> </div>
<style type="text/css">
div:first-child{
font-size: 30px;
color: green;
}
div:last-child{
font-size: 20px;
color: red;
}
</style>
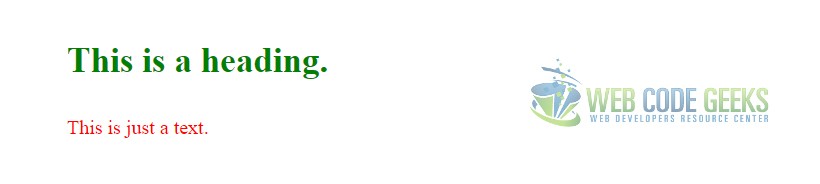
:nth-child(N) – Selects elements based on a simple provided algebraic expression (e.g. “2n” or “4n-1”). Has the ability to do things like select even/odd elements, “every third”, “the first five”, and things like that. Covered in more detail here with a tester tool.
<div> <div><h3>This is a heading.</h3></div> <div><p>This is just a text.</p></div> <div><p>This is just a text.</p></div> <div><p>This is just a text.</p></div> </div>
<style type="text/css">
div:nth-child(3){
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>

:first-of-type – Selects the first element of this type within any parent. So if you have two divs, each had within it a paragraph, image, paragraph, image. Then div img:first-of-type would select the first image inside the first div and the first image inside the second div.
:last-of-type – Same as above, only would select the last image inside the first div and the last image inside the 2nd div.
4. Conclusion
Pseudo-classes, together with pseudo-elements, let you apply a style to an element not only in relation to the content of the document tree, but also in relation to external factors like the history of the navigator (:visited, for example), the status of its content (like :checked on some form elements), or the position of the mouse (like :hover which lets you know if the mouse is over an element or not). Feel free to play around with these pseudo classes to get used to them.
5. Download
You can download the full source code of this example here: CSS Pseudo Class



