CSS Margin Bottom Example
1. Introduction
It is usually a good practice to space out the elements on your web page for easier viewing and readability. CSS provides properties like padding and margin which help with this. They both essentially add space around an HTML element, but with a key difference. While the padding property adds or increases the space between the element and its own border, the margin property adds space outside its own border.
The margin property can be used to add space in all directions around the element – left, right, top and bottom. In this post, we’ll delve deeper into the margin-bottom property.
2. CSS margin-bottom property
As the name suggests, this property sets the bottom margin of an HTML element. Interestingly, its value can be set to positive or negative values – positive values will increase the space/distance between the element and other elements below it, while negative values will have the opposite effect.
2.1 Usage syntax
The value of the margin-bottom property can be either of the following:
- length – This can be in cm, pt, px, em etc. (default = 0)
- percentage – This is the value in percentage
auto– This tells the browser to calculate the bottom margin automaticallyinitial– Sets the property to its default valueinherit– Inherits themargin-bottomvalue from the parent element
2.2 A simple example
Create an HTML file called example.html and paste the following contents into it:
example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>CSS Margin Bottom Example</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./style.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="section1">Section 1</div>
<div class="section2">Section 2</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Next, create a stylesheet called style.css and paste the following contents into it:
style.css
.section1 {
height: 30px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
.section2 {
height: 30px;
}
.wrapper {
border: 1px solid black;
width: 200px;
background-color: gray;
}
div {
width: 200px;
background-color: white;
}
Make sure you have saved both the files, and open example.html in your browser. Here’s what it should look like:
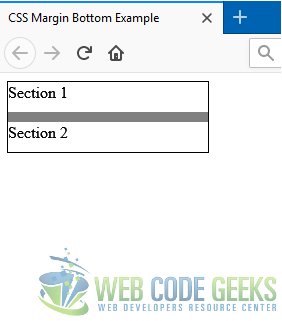
The grey colored area between the two sections represents the space added by the margin-bottom property specified for Section 1. You can play around with its value to see how it affects the spacing between the sections.
3. About collapsing margins
Another interesting point to note, as far as the margin property in general is concerned, is its behavior in case of elements which are adjacent to each other and aligned vertically (top or bottom). In case margin-top and margin-bottom are specified for the elements touching each other, the margin value which is actually applied is the greater of the two specified values.
For example, from the previous example, consider section1 and section2 as stacked vertically with margin-bottom and margin-top specified as 30px and 10px respectively. In this case, the total margin between them will be 30px, instead of 40px which would seem like the logical total value of the margin.
3.1 Collapsing margins in action
As we discussed, let’s re-use the same example.html file from our previous example. Now, modify the margin-bottom value for section1, and add a margin-top property to section2. Your style.css file should look like this (changes are highlighted):
style.css
.section1 {
height: 30px;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
.section2 {
height: 30px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.wrapper {
border: 1px solid black;
width: 200px;
background-color: gray;
}
div {
width: 200px;
background-color: white;
}
Now refresh example.html in your browser. The gray area represents the margin gap, as shown in the below screenshot:
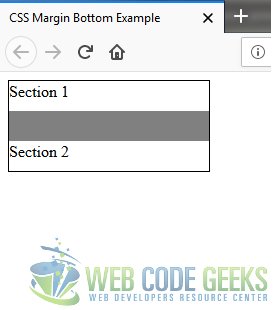
The actual margin between the elements is a total 30px, and not 40px as logic would otherwise suggest.
3.2 Why they are useful
Collapsing margins, though an obscure concept, can come in handy in certain scenarios:
- Empty elements don’t take up their allotted margin area, helping to avoid inconsistent spacing.
- Allow for an increased scope of standardization in declaring margins for various page elements.
- They also apply to elements which are nested.
4. Download the Source Code
This was an example for the CSS margin-bottom property.
You can download the full source code of this example here: CSSMarginBottomExample.zip



