AngularJS HTTP Post Example
Hello readers, in this tutorial, we will learn how to implement the angular library $http.post() method in the angular web applications. For this tutorial, we’ll send an HTTP post request to the web server.
1. Introduction
AngularJS is a JavaScript MVC or Model-view-controller framework developed by Google that lets developers build well structured, easily testable, and maintainable front-end applications. The angular library provides multiple out-of-box services and Angular Ajax is one of them.
The angular framework provides the $http services and is used to do the HTTP request to retrieve the desired data from the server. The server would then make a database call to retrieve the required records in the JSON format. In Angular Ajax, developers can send the Ajax requests in multiple ways, such as:
- Angular Ajax calls through
$httpservice - JSONP calls through
$httpservice - REST API calls

1.1 What are HTTP service?
$http is the core angular service used to do the HTTP requests to communicate with the remote servers and retrieve the required data through the browser’s XMLHttpRequest object or the JSON. To access the Angular Ajax in a controller, developers will have to use the $scope object i.e. $http service sends the data to the web server in the following way.
$http basic syntax
$http({
method : "POST",
url : "<sample_url_path>",
data: form_data,
headers: header_config
}).then(function(response) {
$scope.output_msg = response.data;
});
Where:
- The
methodproperty defines the ‘GET‘ or the ‘POST‘ operator - The
urlproperty is the URL of the HTTP server to perform the required operations - The
dataproperty is used to send the required values to the requested URL - The
headerproperty specifies the ‘content-type‘ - The
$httpservice makes an Ajax call and set the result in theoutput_msgproperty. Later, this model object displays the result inHTML
Do note, the $http service returns the success() and failure() promise objects that take call back functions as parameters.
1.1.1 HTTP Service Methods
There are several functions of calling the $http service. Below is the list of built-in functions available with this service.
$http.get(url, config): This is frequently used method to read the records from the server$http.post(url, data, config)and$http.put(url, data, config): These methods accept an input argument to be sent to the server inJSONstring. The response object of the$http.post()and$http.put()methods has following properties:- Configuration object used to generate the HTTP request
- Response data which can either be a string or an object
- The status code and text of the HTTP response
- Header information
$http.delete(url, config): This method deletes the record or the information from the server$http.head(url, config): This method allows the client and the server to pass an additional information with the request or the response object
Developers can refer this link to have a detailed information on $http service. These new APIs make developer’s life easier, really! But it would be difficult for a beginner to understand this without an example. Therefore, let us create a simple application using the $http.post() method for sending the data to the web server.
2. AngularJS HTTP Post Example
Here is a step-by-step guide for implementing the $http.post() method in angular applications.
2.1 Tools Used
We are using Eclipse Kepler SR2, JDK 8 and Maven. Having said that, we have tested the code against JDK 1.7 and it works well.
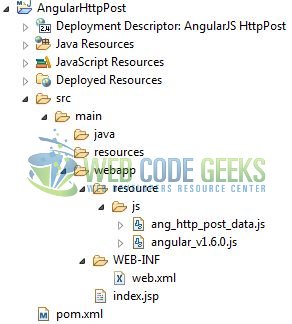
2.2 Project Structure
Firstly, let’s review the final project structure if you are confused about where you should create the corresponding files or folder later!
2.3 Project Creation
This section will show how to create a Java-based Maven project with Eclipse. In Eclipse Ide, go to File -> New -> Maven Project.
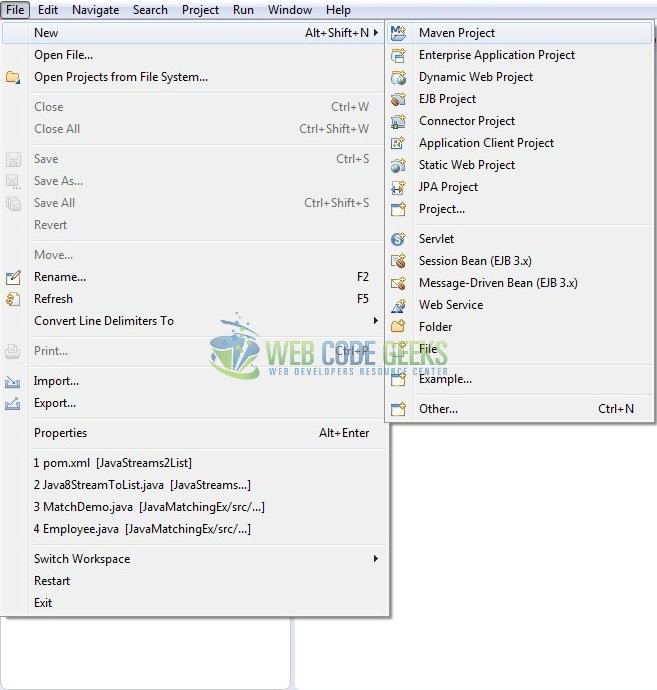
In the New Maven Project window, it will ask you to select project location. By default, ‘Use default workspace location’ will be selected. Just click on next button to proceed.
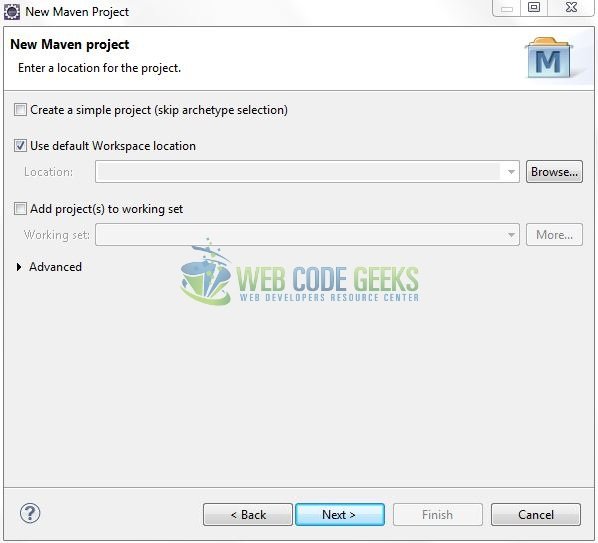
Select the ‘Maven Web App’ Archetype from the list of options and click next.
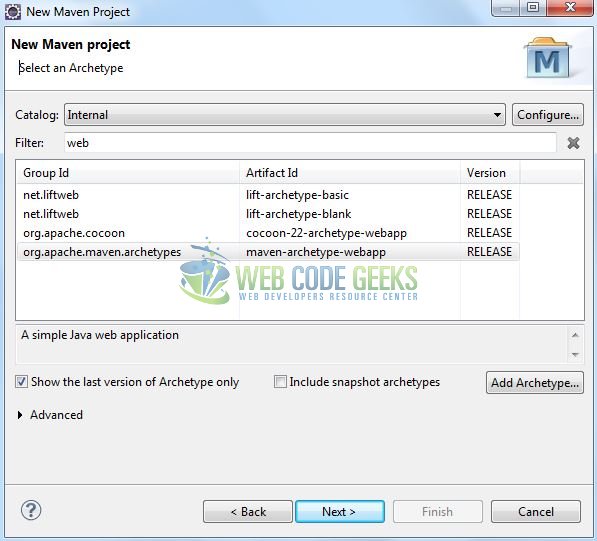
It will ask you to ‘Enter the group and the artifact id for the project’. We will enter the details as shown in the below image. The version number will be by default: 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.
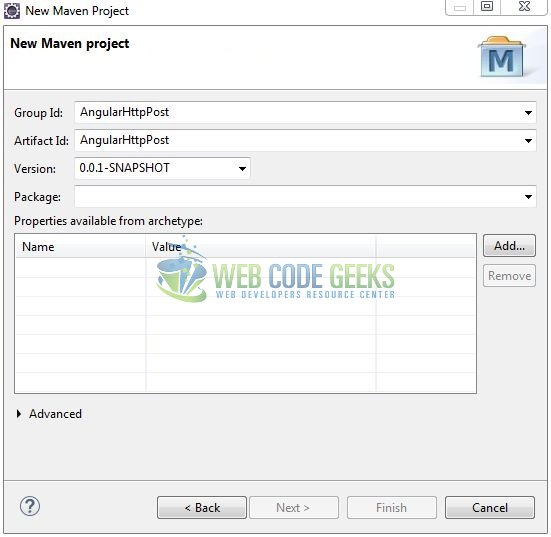
Click on Finish and the creation of a maven project is completed. If you see, it has downloaded the maven dependencies and a pom.xml file will be created. It will have the following code:
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>AngularHttpPost</groupId> <artifactId>AngularHttpPost</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> </project>
Let’s start building the application!
3. Application Building
Let’s create an application to understand the basic building blocks of the $http.post() method in the angular library.
3.1 Load the AngularJS framework
Since it is a pure JavaScript framework, we should add its reference using the <script> tag.
<script type="text/javascript" src="resource/js/angular_v1.6.0.js"></script>
3.2 Define the AngularJS application
Next, we will define the angular application using the <ng-app> and <ng-controller> directives.
index.jsp
<div ng-app = "myApp" ng-controller="ctrl"> ..... </div>
3.3 Creating an AngularJS Controller
The JavaScript file i.e. ang_http_post_data.js includes the ctrl function as the “controller” in the Model-view-controller. This JavaScript code has a function named validateCredentials() which has:
- The data object that contains the serialized value from the
login_idand thelogin_pwdfields of theHTMLform - Config attribute to change the default content-type header of the angular library
$http.post()method to send the asynchronous request to the web server on the specified url and the response data is set into the$scope.output_msgproperty
ang_http_post_data.js
var app = angular.module("app", []);
app.controller("ctrl", ['$scope', '$http', function($scope, $http) {
$scope.output_msg = null;
// Use $.param jQuery function to serialize data from JSON
var form_data = $.param({
id: $scope.login_id,
pwd: $scope.login_pwd
});
var header_config = {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8;'
}
};
$scope.validateCredentials = function() {
$http({
method: 'POST',
url: '<sample_application_path>/samplepost',
data: form_data,
config: header_config
}).then(
function(response) {
$scope.output_msg = response.data.msg;
angular.element(document.getElementById("msg")).css("color", "green");
console.log("Status Code= " + response.status + ", Status Text= " + response.statusText);
},
function(response) {
$scope.output_msg = "Service unavailable. Please try again.";
angular.element(document.getElementById("msg")).css("color", "red");
console.log("Status Code= " + response.status + ", Status Text= " + response.statusText);
});
};
}]);
3.4 Complete Application
Complete the above steps and I will show you how to use the Angular Ajax with real-life practices. Let’s see the HTML code snippet which has two text-boxes and a submit button to post the data to the web server.
index.jsp
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>AngularJS HttpPost</title>
<!-- jQuery File -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.js"></script>
<!-- AngularJs File -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="resource/js/angular_v1.6.0.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="resource/js/ang_http_post_data.js"></script>
<!-- Bootstrap Css -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="angularHttpPost" class="container">
<h1 align="center" class="text-primary">AngularJS - HTTP Post Example</h1>
<hr />
<!------ ANGULAR JS HTTP 'Post()' EXAMPLE ------>
<div ng-app="app" ng-controller="ctrl">
<h3 id="header_msg" class="text-warning">A demo of HTTP '<em>post()</em>' method in Angular JavaScript!</h3>
<div> </div>
<!----- CREDENTIALS FORM ------>
<div class="input-group col-xs-4">
<span class="input-group-addon"><i class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></i></span>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="lid" placeholder="Enter login id ..." name="login_id" ng-model="login_id" required="required" maxlength="6">
</div>
<div> </div>
<div class="input-group col-xs-4">
<span class="input-group-addon"><i class="glyphicon glyphicon-lock"></i></span>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="lpwd" placeholder="Enter password ..." name="login_pwd" ng-model="login_pwd" required="required">
</div>
<small id="loginHelp" class="form-text text-muted"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-asterisk"></span>Validate your login credentials.</small>
<!----- SUBMIT BUTTON ------>
<div> </div>
<button id="submit_btn" class="btn btn-primary" ng-click="validateCredentials()">Validate</button>
<!----- SUCCESS / ERROR MESSAGE ------>
<div> </div>
<div id="msg">{{ output_msg }}</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
4. Run the Application
As we are ready for all the changes, let us compile the project and deploy the application on the Tomcat7 server. To deploy the application on Tomat7, right-click on the project and navigate to Run as -> Run on Server.
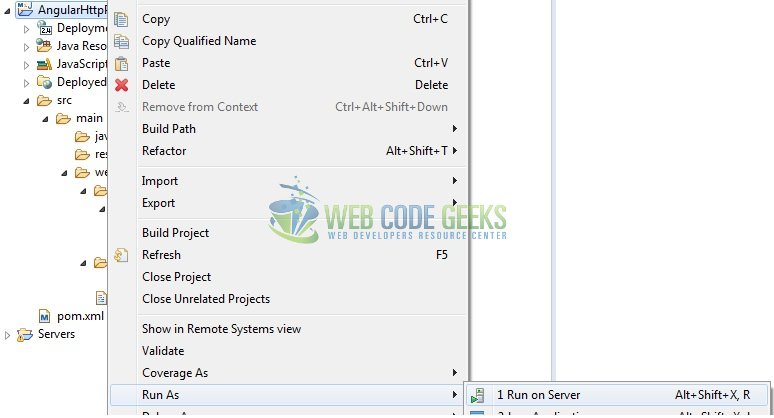
Tomcat will deploy the application in its web-apps folder and shall start its execution to deploy the project so that we can go ahead and test it in the browser.
5. Project Demo
Open your favorite browser and hit the following URL. The output page using the angular ajax will be displayed.
http://localhost:8080/AngularHttpPost/
Server name (localhost) and port (8080) may vary as per your Tomcat configuration.
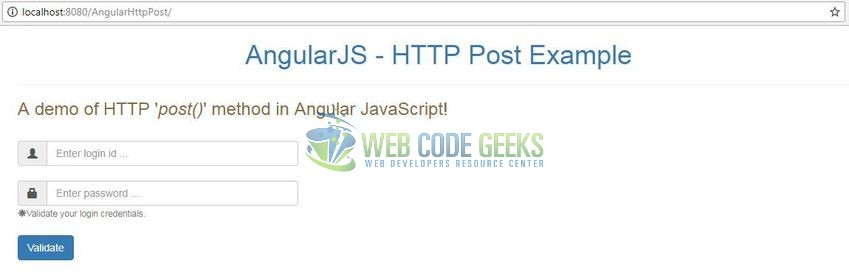
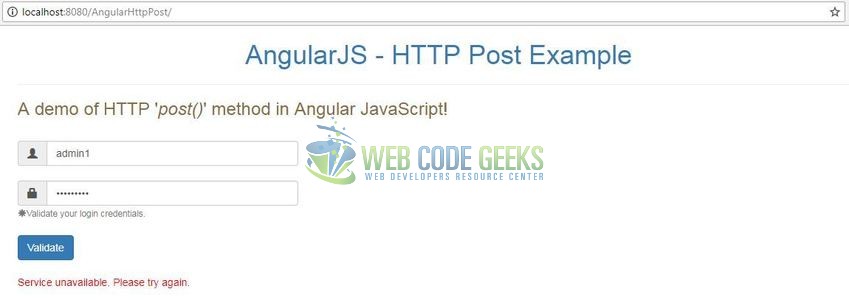
Here, if the login credentials are successfully validated, the users will get a success message as shown in Fig. 9

If the server URL is not responding, the user will get an error message as shown in Fig. 10.
That’s all for this post. Happy Learning!!
6. Conclusion
In this section, developers learned how to create a simple application using the $http.post() method. Developers can download the sample application as an Eclipse project in the Downloads section.
7. Download the Eclipse Project
This was a tutorial of the $http.post() method in the angular library.
You can download the full source code of this example here: AngularHttpPost



