JavaScript Events Tutorial
Greetings readers, in this tutorial, we will show how to use the JavaScript Events.
1. Introduction
JavaScript is an object-oriented programming language that allows the client-side scripting to interact with a user and deliver the dynamic pages. Most web browsers including Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, Internet Explorer, Microsoft Edge, Opera, etc. support it. The JavaScript scripting language includes:
- Declaring variables
- Maintaining the retrieving values
- Defining and invoking functions
- Defining classes
- Load and use external modules
- Define event handlers
- And much more ….
Table Of Contents
1.1 Advantages of JavaScript Language
The pros of using the JavaScript scripting language are:
- JavaScript is easy to learn
- It executes on client’s browser, so eliminates the server-side processing and be executed on any OS
- JavaScript can be used with any type of web page e.g. PHP, ASP.NET, Perl etc
- Web-page performance increases due to client-side execution
- JavaScript code can be minified to decrease the loading time from the server
- Many JavaScript-based application frameworks are available in the market to create Single page web applications e.g. AngularJS, ReactJS etc.
1.2 Disadvantages of JavaScript Language
The cons of using the JavaScript scripting language are:
- No support for networking applications
- Does not have any multi-threading or multi-processing capabilities
- Does not allow the file reading and writing capabilities
1.3 Events in JavaScript
- An event is a signal from the browser that something has happened or something that a user does.
- For e.g.:
- A webpage or an image has finished loading
- An input field is changed
- A button is clicked
- Move the cursor over an HTML element
- Submitting an HTML form
- Keystrokes
- Javascript language provides several ways to connect an event handler to an event. These ways are:
- Using HTML tag attributes
- Using DOM object property
- Using special methods such as
addeventlistener()
1.3.1 Common Events in JavaScript
There are sufficient javascript events available to make a webpage dynamic and clean. Here is the list of most common and popular javascript event handlers.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
onchange | Occurs when an HTML element is changed |
onclick | Occurs when the user clicks on an HTML element |
onmouseover | Occurs when the user moves the mouse cursor over an HTML element |
onmouseout | Occurs when the user moves the mouse cursor away from an HTML element |
onkeydown | Occurs when the user pushes a keyboard key |
onload | Occurs when the current web page has finished loading |
2. JavaScript Events Tutorial
Here is a systematic guide for implementing this tutorial using the JavaScript language.
2.1 Tools Used
We are using Eclipse Kepler SR2, JDK 8 and Maven. Having said that, we have tested the code against JDK 1.7 and it works well.
2.2 Project Structure
Firstly, let us review the final project structure if you are confused about where you should create the corresponding files or folder later!
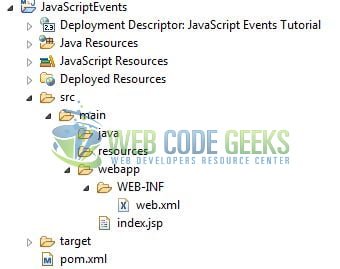
2.3 Project Creation
This section will show on how to create a Java-based Maven project with Eclipse. In Eclipse Ide, go to File -> New -> Maven Project.
In the New Maven Project window, it will ask you to select the project location. By default, ‘Use default workspace location’ will be selected. Just click on the next button to proceed.
Select the ‘Maven Web App’ Archetype from the list of options and click next.
It will ask you to ‘Enter the group and the artifact id for the project’. We will input the details as shown in the below image. The version number will be by default: 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.
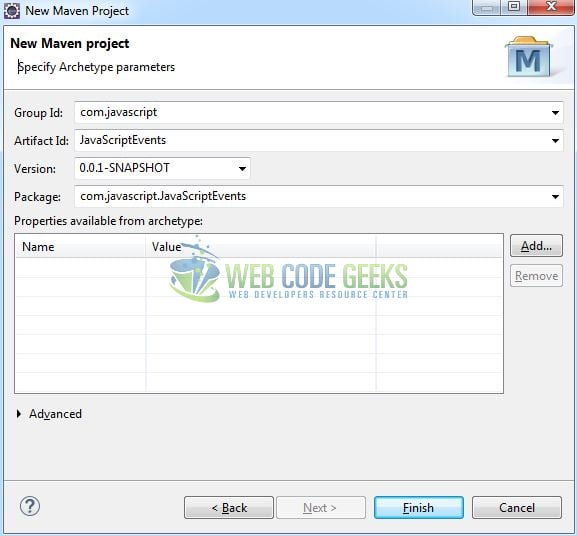
Click on Finish and the creation of a maven project is completed. If you see, it has downloaded the maven dependencies and a pom.xml file will be created. It will have the following code:
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.javascript</groupId> <artifactId>JavaScriptEvents</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> </project>
3. Application Building
Let us create an application to understand the basic building blocks of this tutorial.
3.1 Define the HTML
Let us write a simple index page in the JavaScriptEvents/src/main/webapp/ folder. Add the following code to it:
index.jsp
<!-- Javascript events tutorial -->
<div class="form-group">
<div id="event">
<h4 class="text-primary font-weight-bold">What is an event?</h4>
<ol class="text-info line-hgt">
<li>An event is a signal from the browser that something has happened or something that a user does</li>
<li>For e.g.:
<ul>
<li>A webpage has finished loading</li>
<li>An input field is changed</li>
<li>A button is clicked</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>Javascript language provides several ways to connect an event handler to an event. These ways are:
<ul>
<li>Using HTML tag attributes</li>
<li>Using DOM object property</li>
<li>Using special methods such as <code>addeventlistener()</code></li>
</ul>
</li>
</ol>
</div>
<!-- Input form -->
<div id="code">
<h4 class="text-sucess">Code Snippet</h4>
<div> </div>
<div id="myform">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="name" onblur="validate('name')">
</div>
<button id="btn_submit" type="button" class="btn btn-default" onmouseover="mouseover();" onmouseout="mouseout();" onclick="submit();">Submit</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div> </div>
<!-- Result -->
<h5 id="result" class="text-info"></h5>
3.2 Define the JavaScript function
Let us write a simple javascript function that shows the events implementation in the javascript language. Add the following code to it:
JavaScript function
// Mouseover function
function mouseover() {
var mover = document.getElementById("btn_submit");
mover.style.background= 'blueviolet';
mover.style.color= 'white';
}
// Mouseout function
function mouseout() {
var mout = document.getElementById("btn_submit");
mout.style.background= 'gainsboro';
mout.style.color= 'black';
}
// Blur function
function validate(id) {
var input = document.getElementById(id);
if (input.value == "") {
input.style.color= '#e52213';
input.style.border= 'solid';
} else {
input.style.color= '#00ff99';
input.style.border= 'solid';
}
}
// Form submit function
function submit() {
alert("Form submitted.");
}
3.3 First application
Complete the above steps and save the file. Let us see the sample code snippet.
index.jsp
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Index page</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://www.webcodegeeks.com/wp-content/litespeed/localres/aHR0cHM6Ly9zdGFja3BhdGguYm9vdHN0cmFwY2RuLmNvbS8=bootstrap/4.1.3/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<style>
#event,
#code,
#result {
margin-left: 16px;
}
.line-hgt {
line-height: 2.0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h2 align="center" class="text-danger">Events in JavaScript</h2>
<hr />
<!-- Javascript events tutorial -->
<div class="form-group">
<div id="event">
<h4 class="text-primary font-weight-bold">What is an event?</h4>
<ol class="text-info line-hgt">
<li>An event is a signal from the browser that something has happened or something that a user does.</li>
<li>For e.g.:
<ul>
<li>A webpage has finished loading</li>
<li>An input field is changed</li>
<li>A button is clicked</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>Javascript language provides several ways to connect an event handler to an event. These ways are:
<ul>
<li>Using HTML tag attributes</li>
<li>Using DOM object property</li>
<li>Using special methods such as <code>addeventlistener()</code></li>
</ul>
</li>
</ol>
</div>
<!-- Input form -->
<div id="code">
<h4 class="text-sucess">Code Snippet</h4>
<div> </div>
<div id="myform">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="name" onblur="validate('name')">
</div>
<button id="btn_submit" type="button" class="btn btn-default" onmouseover="mouseover();" onmouseout="mouseout();" onclick="submit();">Submit</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div> </div>
<!-- Result -->
<h5 id="result" class="text-info"></h5>
</div>
<script>
// Mouseover function
function mouseover() {
var mover = document.getElementById("btn_submit");
mover.style.background= 'blueviolet';
mover.style.color= 'white';
}
// Mouseout function
function mouseout() {
var mout = document.getElementById("btn_submit");
mout.style.background= 'gainsboro';
mout.style.color= 'black';
}
// Blur function
function validate(id) {
var input = document.getElementById(id);
if (input.value == "") {
input.style.color= '#e52213';
input.style.border= 'solid';
} else {
input.style.color= '#00ff99';
input.style.border= 'solid';
}
}
// Form submit function
function submit() {
alert("Form submitted.");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
4. Run the Application
As we are ready for all the changes, let us compile the project and deploy the application on the Tomcat7 server. To deploy the application on Tomat7, right-click on the project and navigate to Run as -> Run on Server.
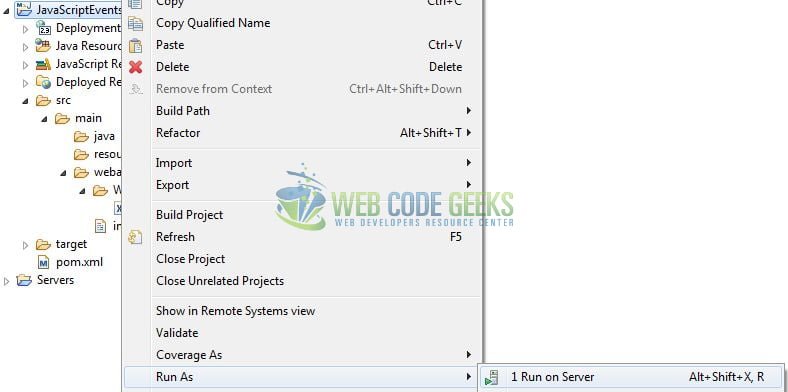
Tomcat will deploy the application in its web-apps folder and shall start its execution to deploy the project so that we can go ahead and test it in the browser.
5. Project Demo
Open your favorite browser and hit the following URL to display the application’s index page as shown in Fig. 7.
http://localhost:8082/JavaScriptEvents/
Server name (localhost) and port (8082) may vary as per your Tomcat configuration.
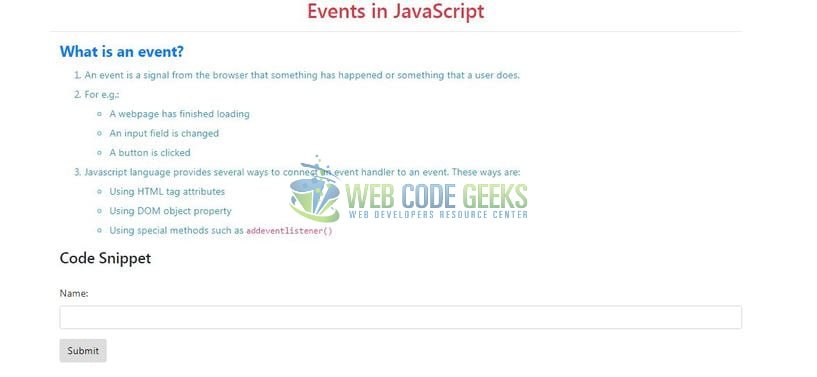
That is all for this tutorial and I hope the article served you whatever you were looking for. Happy Learning and do not forget to share!
6. Conclusion
In this section, developers learned how to create a simple application with the JavaScript language. Developers can download the sample application as an Eclipse project in the Downloads section.
7. Download the Eclipse Project
This was an example of JavaScript Events for beginners.
You can download the full source code of this example here: JavaScriptEvents



